If the properties of a single coating treatment do not fulfil all the requirements of a certain component, coating systems (also known as duplex systems or duplex treatments) can be a viable solution. In the galvanising industry, duplex stands for the combination of zinc electroplating and one or more coatings; however, even coating systems without zinc are possible.
Numerous combination possibilities for different functional and optical requirements for example:
- Zinc and CDC (cathodic dip coating)
- Zinc-Nickel and CDC
- Zinc-Iron and CDC
- CDC and powder coating
- Zinc, Zinc-nickel, Zinc-iron, CDC and powder
- electroless nickel and silver
- electroless nickel and tin
- nickel (galvanic) and tin
- nickel and silver
Zinc, Zinc-nickel or Zinc-iron with CDC
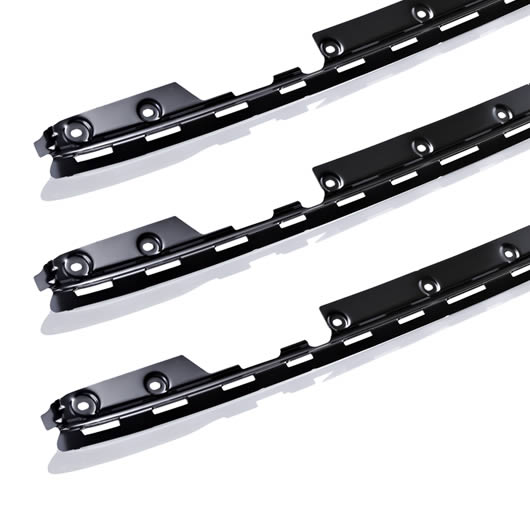
The combination of functional surfaces such as zinc, zinc-nickel or zinc-iron with CDC is especially popular in the automobile industry:
- CDC top layer for a visually attractive, even black surface Zinc electroplating for high corrosion protection
- Durable, abrasive-resistant zinc- or zinc-nickel surface prevents rust creepage
- The coating system withstands much higher stresses than the individual systems
- Distinctly higher corrosion resistance than simple zn- or zn-ni systems
- Examples of usage: locking parts for automobile sun roofs, parts for panorama roofs, etc.
CDP and powder
A combination of CDC and powder also creates added value:
- Visual improvement of the coating system achieved through powder coating
- All colours of the RAL-spectrum can be implemented
- Depending on the colour chosen, the powder coating may be UV-resistant
- Powder coating – even if light colours are chosen – completely covers black CDP layer
- CDP layer ensures higher corrosion protection, especially at the edges
Electroless nickel (nickel-phosphorous) and silver
Electroless nickel can also be used in coating systems. These combined surface systems are highly suitable for parts with complex geometries (i.e. undercuts, back tapers) and with high demands regarding both dimensional accuracy and layer thickness.
- Distinctly higher corrosion resistance than the individual systems
- Electroless nickel serves as a barrier coat and prevents diffusion of silver into the base material
- Silver considerably improves electrical conductivity
- Highly reduced transition resistance due to silver layer
Electroless nickel (nickel-phosphorous) and tin
- Increased corrosion resistance compared to single layers
- Nickel-phosporous operates as a barrier coat and prevents diffusion of tin into the base material as well as oxidation of the basic material
- Electroless nickel inhibits whisker formation of non-ferrous metals
- Tin improves electrical conductivity
- Tin also effects a better solderability
Galvanic nickel and tin
Galvanic nickel can be combined with further surfaces, if parts have no complex geometry and no special demands regarding dimensional accuracy and layer thickness.
- Improved corrosions resistance compared to single layers
- Nickel (galvanic) acts as a barrier layer between base material (especially non-ferrous metal) and tin
- Tin improves both electrical conductivity and solderability
Galvanic nickel and silver
- Improved corrosions resistance compared to single layers
- Nickel (galvanic) acts as a barrier layer between base material (especially non-ferrous metal) and silver, depending on the substrate/base material
- Silver considerably improves electrical conductivity
Coating systems can be applied both as rack and barrel plating, depending on the disposed surface.

















 Holzapfel Group
Holzapfel Group YouTube
YouTube